Introduction
A bit about cloning and vectors
What is cloning?
Cloning is the creation of an organism that is an exact genetic copy of another.
What is a vector?
A vector is a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to transfer foreign genetic material into another cell.
It is basically of two types:
- Cloning vector
- Expression vector
- A cloning vector is a DNA molecule that has an origin of replication and is capable of replicating in a bacterial cell.
- Expression vector is a plasmid containing the required regulatory sequences specifically used for the expression of a particular gene into proteins within the target cell.[2]
Most vectors are genetically engineered plasmids or phages. But cosmid vectors, bacterial artificial chromosomes, and yeast artificial chromosomes are also used.
The vector used must harbour a suitable marker gene whose activity in the target cell can facilitate the identification of cells carrying it
- Antibiotic resistance-conferring markers
- Unmodified (wild-type) host must be sensitive the the chosen antibiotic
- Ampicillin
- Tetracycline
- Chloramphenicol
Few of the generally used cloning vectors include:
- Plasmids
- Bacterophages
- Cosmids
- Yeast artifical chromosomes (YAC's)
- Bacterial arifical chromosomes (BAC's)
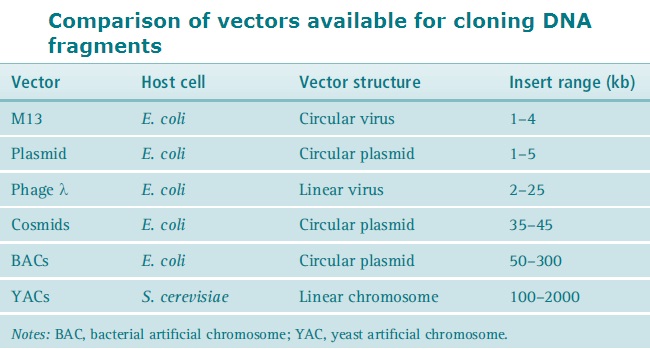
Image courtesy: Table 6.2, Principles and Techniques of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology , Wilson Keith and Walker John, seventh edition, cambridge university press, 2010
- Principles of gene manupulations,S.B. Primrose, R.M.Twyman and R.W.Old, sixth edition, blackwell science.2004
- http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Expression_vector
- Principles and Techniques of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology , Wilson Keith and Walker John, seventh edition, cambridge university press, 2010