Phagemids
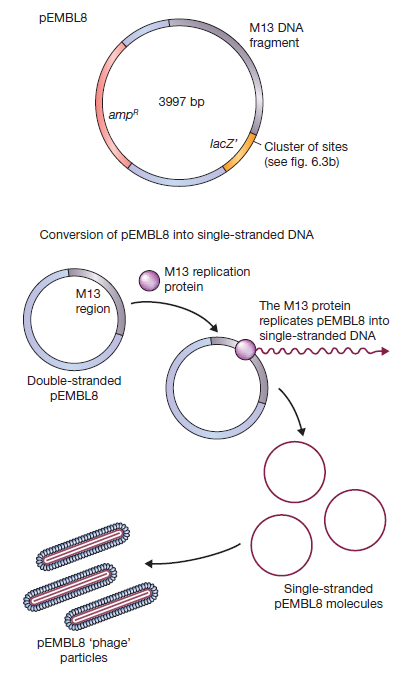
The sort coming of M13 phage were overcome by bulding another vector ie Phagemids.A popular example of phagmids is pEMBL8.[4]
pEMBL8 was made by transferring into pUC8 a 1300 bp fragment of the M13 genome.[4] This piece of M13 DNA contains the signal sequence recognized by the enzymes that convert the normal double-stranded M13 molecule into single-stranded DNA before secretion of new phage particles. [4] This signal sequence is still functional even though detached from the rest of the M13 genome, so pEMBL8 molecules are also converted into single-stranded DNA and secreted as defective phage particles. All that is necessary is that the E. coli cells used as hosts for a pEMBL8 cloning experiment are subsequently infected with normal M13 to act as a helper phage, providing the necessary replicative enzymes and phage coat proteins. pEMBL8, being derived from pUC8, has the polylinker cloning sites within the lacZ′ gene, so recombinant plaques can be identified in the standard way on agar containing X-gal. With pEMBL8, single-stranded versions of cloned DNA fragments up to 10 kb in length can be obtained, greatly extending the range of the M13 cloning system. [4]
Image courtesy: fig 6.8, Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis- An Introduction, T.A.Brown. fifth edition, blackwell publishing, 2010
Reference:
- Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis- An Introduction, T.A.Brown. fifth edition, blackwell publishing, 2006