M13 vector
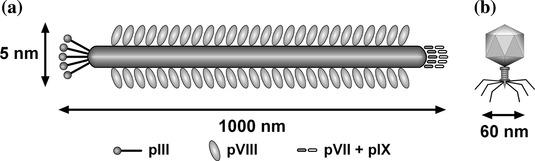
Image source: http://www.springerimages.com/img/Images/Springer/PUB=Springer_Netherlands-Dordrecht/JOU=10989/VOL=2006.12/ISU=1/ART=2005_9002/MediaObjects/MEDIUM_10989_2005_9002_Fig2_HTML.jpg
M13 is an example of a filamentous phage and is completely different in structure from λ . [4] Furthermore, the M13 DNA molecule is much smaller than the λ genome, being only 6407 nucleotides in length. [4] It is circular and is unusual in that it consists entirely of single-stranded DNA. M13 follows a simpler infection cycle than λ, and does not need genes for insertion into the host genome. [4]
Features of M13[4]
1. The genome is less than 10 kb in size
2. the double-stranded replicative form (RF) of the M13 genome behaves very much like a plasmid
3. It is easily prepared from a culture of infected E. coli cells
4. genes cloned with an M13-based vector can be obtained in the form of single-stranded DNA.
The normal M13 genome is 6.4 kb in length but most of this is taken up by ten closely packed genes each essential for the replication of the phage. [4] There is only a single 507-nucleotide intergenic sequence into which new DNA could be inserted without disrupting one of these genes, and this region includes the replication origin which must remain intact. [4]
The first step in construction of an M13 cloning vector was to introduce the lacZ' gene. This gave rise to M13mpl, which forms blue plaques on X-gal agar. [4] M13mpl does not possess any unique restriction sites in the lacZ' gene. [4] It does, however, contain the hexanucleotide GGATTC near the start of the gene. [4]
An alteration was carried out using in vitro mutagenesis, resulting in M13mp2. [4] M13mp2 has a slightly altered laeZ' gene M13mp2 is the simplest M13 cloning vector. [4]
The next step in the development of M13 vectors was to introduce additional restriction sites into the laeZ' gene. [4] This was achieved by synthesizing in the test tube a short oligonucleotide, called a polylinker, that consists of a series of restriction siteS and has EcoRI sticky ends This polylinker was inserted into the EeoRI site of IV M13mp2, to give M13mp7. [4]
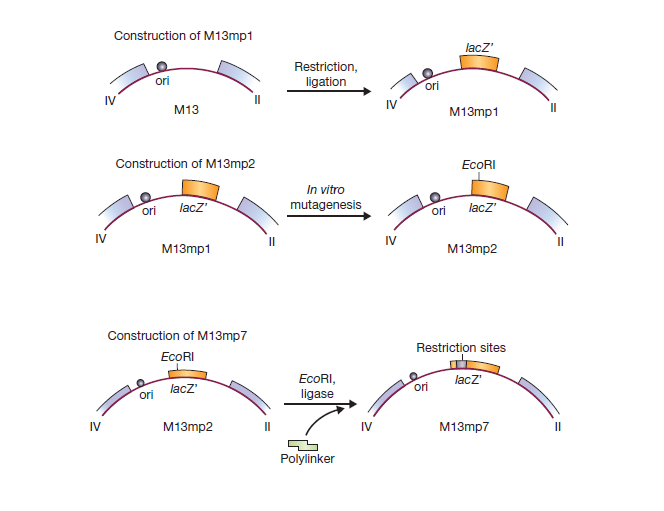
Image source: Fig 6.6 Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis- An Introduction, T.A.Brown. fifth edition, blackwell publishing, 2010