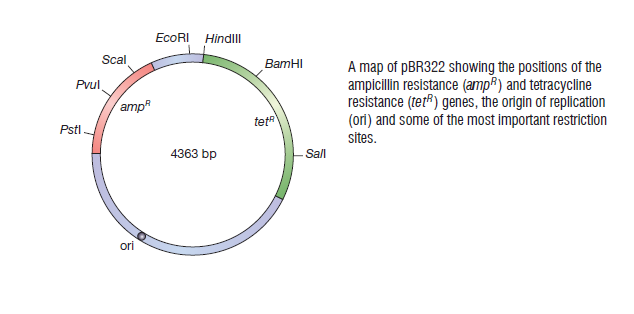
pBR322 an example of plasmid vector
pBR332
Image courtesy: Fig 6.1, Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis- An Introduction, T.A.Brown. fifth edition, blackwell publishing, 2010
One of the most notable plasmids, termed pBR322 after its developers Bolivar and Rodriguez (pBR)[5] pBR322, have a relaxed origin of replication, whose activity is not tightly linked to cell division. Hence a large number of plasmid molecules will be produced per cell.[5]
The cloning vectors that were used in early cloning experiments were natural plasmids like Col E1 and pSC101. These plasmids are small and have single sites for the common restriction endonucleases so they have limited genetic markers for selecting transformants. To overcome this considerable effort was made to construct cloning vectors. The most widely used of the early purpose-built vectors is pBR322. pBR322 comprise of DNA derived from three different naturally occurring plasmids. The ampR gene originally residing on plasmid R1, tetR from R6-5. The replication origin of pBR322, which directs multiplication of the cloning vector in host cells is originally from pMB1.[4]
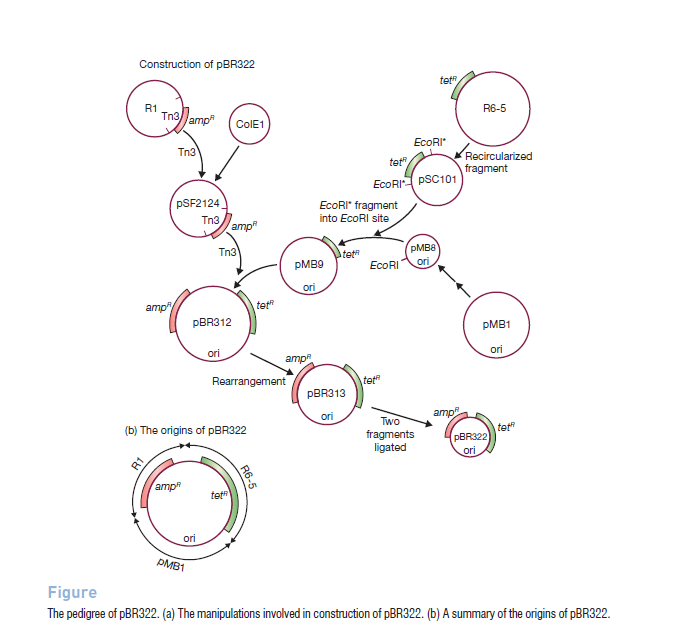
Image courtesy: Fig 6.2, Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis- An Introduction, T.A.Brown. fifth edition, blackwell publishing, 2010
Plasmid pBR322 has been completely sequenced. [5] It characterizes pBR322 in terms of its restriction sites i.e. exact length of every fragment can be calculated. These fragments can serve as DNA markers for sizing any other DNA.It can be purified with ease and so can the recombinant DNA molecules constituted within it.
There are over 40 enzymes with unique cleavage sites on the pBR322 genome. [5] The target sites of 11 of these enzymes lie within the TcR gene, and there are sites for a further two within the promoter of that gene. There are unique sites for six enzymes within the ApR gene. [5] Cloning can be done in pBR322 with the aid of any one of those 19 enzymes will result in insertional inactivation of either the ApR or the TcR markers. However, cloning in the other unique sites does not permit the easy selection of recombinants, because neither of the antibiotic resistance determinants is inactivated. [5]
One of the advantages of pBR322 is that it has a high copy number.Thus an E.coli culture provies a good yield of recombinant pBR322 molecule.[4]
In practice, transformants are selected on the basis of their Ap resistance and then replica-plated on to Tc-containing media to identify those that are TcS. Transformants are selected on rich medium containing soluble starch and Tc. When colonized plates are flooded with an indicator solution of iodine and penicillin, â-lactamase-producing (ApR) colonies clear the indicator solution whereas ApS colonies do not. Plasmid pBR322 has been a widely used cloning vehicle. The popularity of pBR322 is a direct result of the availability of an extensive body of information on its structure and function. This in turn is increased with each new study.
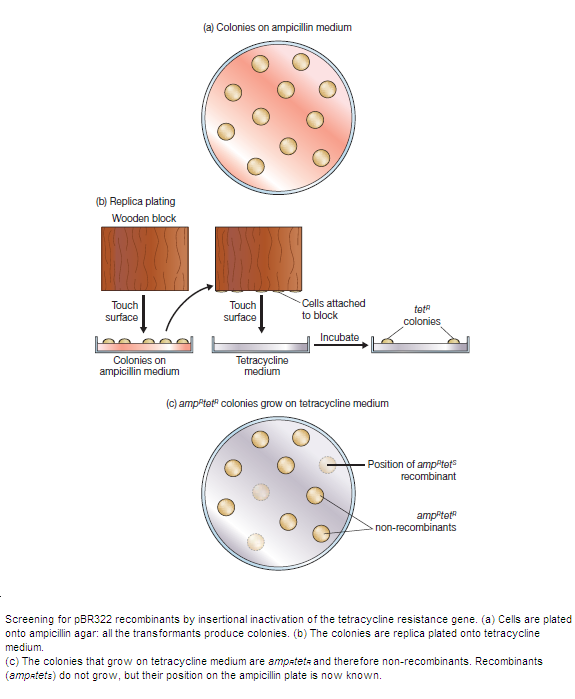
Image courtesy: Fig 5.8, Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis- An Introduction, T.A.Brown. fifth edition, blackwell publishing, 2010
Other E.coli plasmid cloning vectors
Many other plasmid cloning vectors have been constructed, the majority of which derived from pBR322 plasmid.[26]
pBR327 plasmid
It is a higher copy number plasmid and was constructed by removing a 1089 bp segment from pBR322. This deletion left the ampR tetR genes intact, but changed the replicative and conjugative abilities of the resulting plasmid.[26]
Comparison between pBR322 and pBR327
- pBR327 has a higher copy number(30-45 molecules) than pBR322. The higher copy number of pBR327 in normal cells makes this vector more suitable.[26]
- The deletion also destroys the conjugative ability of pBR322, making pBR327 a non-conjugative plasmid that can't direct its own transfer to other E.colicells.[26]
Advantages:
- Much smaller insert site (~6kb)
- Detection is much simpler, reliable.
- Higher copy number i.e. 15 copies per cell
- Model system for understanding translation and transcription of prokaryotes.
- Conjugative
- Detection scheme takes time
- Selective pressure
- Size of insert is only 6kb
Reference:
- Principles and Techniques of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology , Wilson Keith and Walker John, seventh edition, cambridge university press, 2010
- Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis- An Introduction, T.A.Brown. fifth edition, blackwell publishing, 2010